Cryptocurrency mining is a complex and energy-intensive process of verifying transactions on a blockchain network and adding them to the blockchain’s public ledger or distributed ledger. It plays a vital role in securing and decentralizing the cryptocurrency network by preventing double spending and authenticating transactions. Miners are incentivized to secure the network by participating in the transaction validation process, thereby increasing their chances of earning newly issued coins.
Miners maintain and secure the blockchain, the blockchain rewards coins, and coins incentivize miners to maintain the blockchain. The mining process involves large, decentralized computer networks around the world that verify and secure blockchains, which record cryptocurrency transactions. In exchange for their processing power, computers on the network are rewarded with new coins.
Miners receive rewards for their work in cryptocurrency tokens, which motivates everyone to contribute to the main goal of mining:
legalize and monitor Bitcoin transactions. Bitcoin is a “decentralized” cryptocurrency because it does not depend on any central authority such as a central bank or government to oversee its regulation. High-powered computers compete to be the first to validate a series of transactions called a block and add that block to the blockchain.
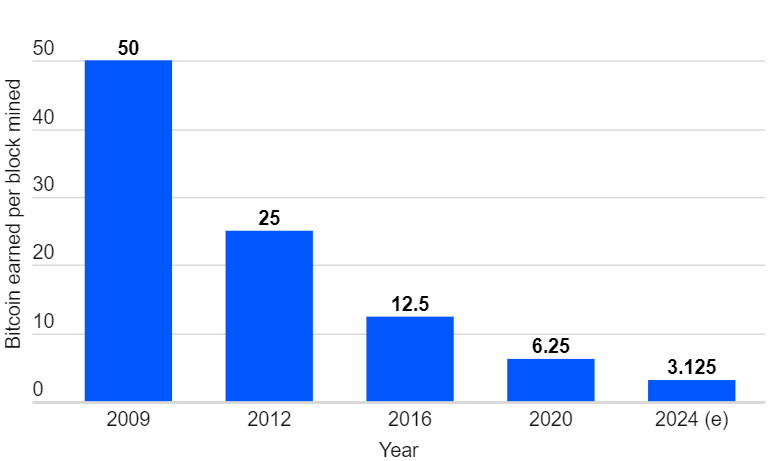
Miners receive transaction fees and 6.25 BTC per block for their effort (if they solve the right block), which amounts to about $147,000 at current prices.
Does Cryptocurrency mining work?
Cryptocurrency mining is a profitable way to earn cryptocurrencies, but is not always profitable due to factors such as cryptocurrency prices, electricity costs, and mining network difficulty. As more miners join the network, the difficulty of mining increases, making it more difficult and expensive to mine cryptocurrency profitably.
There are three main ways to get Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies:
buy them on exchanges like Coinbase, receive them as payment for goods or services, or “mine” them virtually. Bitcoin mining requires specialized computers to perform the necessary calculations to verify and record each new Bitcoin transaction and ensure the security of the blockchain. This requires a large amount of computing power, which is provided voluntarily by miners.
Bitcoin mining is like operating a large data center, in that companies buy the mining hardware and pay for the electricity needed to operate it. For this to be profitable, the value of the coins earned must be greater than the cost of mining those coins. Miners are motivated by a lottery in which each computer on the network races to be the first to guess a 64-digit hexadecimal number called a “hash.” The faster the computer can guess, the more likely the miner is to win the reward.
Today, cryptocurrency mining requires a dedicated GPU or application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) miner, always connected to a reliable Internet connection. Everyone who mines cryptocurrency must also be a member of an online cryptocurrency mining pool. To successfully add a block to the blockchain, miners must compete to solve extremely complex mathematical problems that require the use of expensive computers and huge amounts of electricity.
The processing power needed to mine bitcoin requires access to powerful computers and large amounts of electricity. Bitcoin mining was initially performed by individuals on single computers, but as the difficulty of solving the algorithms involved in transactions increased over time, it is now highly unlikely that Personal computers can mine Bitcoin. As the difficulty of cryptocurrency mining has increased, most Bitcoin miners have turned to application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) and other methods to mine Bitcoin.

The history of Cryptocurrency mining
Bitcoin mining has evolved significantly, transitioning from standard CPUs to GPUs and ASIC miners, enhancing efficiency and specialized in the industry.
CPU mining :
CPU mining, an important part of Bitcoin mining, was previously a low-cost alternative for the majority of miners. However, as the hash rate of the network expanded, profitable mining became more difficult. CPU mining became practically impossible with the introduction of specialized hardware and the increasing difficulty of mining. Because of the enormous expenses and difficulty, CPU mining is now practically impractical.
GPU mining:
GPUs, which were meant for graphics-intensive activities, can now be utilized to mine altcoins. They provide computing power and energy efficiency, making them a more cost-effective and versatile alternative to ASIC mining hardware. Mining efficiency is determined on the complexity and algorithm, while GPU mining maximizes processing capability by integrating GPUs into a single setup.
ASIC mining:
ASIC miners, custom hardware designed for bitcoin mining, have revolutionized the industry by providing unparalleled computing power and energy efficiency. These specialized machines, unlike GPU miners, produce more units of cryptocurrency than GPUs. However, ASIC mining is expensive, making it one of the most expensive ways to mine. As mining difficulty increases, older ASIC models become unprofitable and require frequent replacement. Large-scale mining operations with access to cheap electricity and specialized ASIC miners currently dominate the market. ASIC mining is a significant advancement in mining technology, making it a competitive and centralized method for mining cryptocurrencies.
Is Cryptocurrency Mining legal?
Cryptocurrency Mining is legal in most countries, but some are banned or restricted due to its decentralized nature, volatility, and high power consumption. Countries like China, Russia, Bolivia, Algeria, and Ecuador have banned or outright illegal bitcoin trading due to its decentralized nature, volatile value, and association with criminal activities. EU countries like Finland, Germany, France, the United States, Canada, Australia, and the UAE welcome bitcoin, while only El Salvador has adopted it as legal tender.
Is cryptocurrency mining profitable?
Cryptocurrency mining offers many benefits, such as earning cryptocurrencies without investing money, securing and decentralizing the cryptocurrency network, and increasing the demand for cryptocurrencies. However, it is important to understand the risks involved before you start mining cryptocurrency.
The benefits of cryptocurrency mining include profit potential, the security of the blockchain, and incentives for miners to contribute their computing power to the network. However, it also uses a lot of energy and can be expensive. Cryptocurrency mining is competitive and mining difficulty increases as more miners join the network. The profitability of cryptocurrency mining depends on factors such as the hash rate of the mining rig, power consumption, and overall costs. Mining hardware can be expensive, so miners must balance the cost with the potential rewards it can generate. Electricity costs can exceed revenue and make mining unprofitable.
Miners should also consider the difficulty level of the cryptocurrency they want to mine, as high upfront costs and ongoing electricity costs can make mining unprofitable. Additionally, changes at the protocol level, such as the Bitcoin halving or Ethereum’s move from a Proof of Stake to Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, could affect mining profitability. Participating in proof-of-work cryptocurrency requires knowledge, resources, and risk tolerance to cover initial and ongoing costs. By understanding the process, considering the legal and environmental implications, and considering the financial risks, individuals can join the ranks of miners operating proof-of-work cryptocurrencies.
Risks and Limitations:
Bitcoin mining is a lucrative enterprise that comes with its own set of constraints and risks. It can introduce security flaws, ensure success with little ROI, and raise electricity and processing costs. Cryptocurrencies are volatile, and there are no government laws or legal safeguards in place. Cryptocurrencies are not widely acknowledged, and transactions are irrevocable. Price fluctuation has made it difficult for miners to decide if the benefits exceed the risks. Governments have been slow to accept cryptocurrencies, leading to skepticism and possibly legalization, as witnessed in China in 2021.
Cryptocurrency mining uses processing power to verify transactions and safeguard blockchain networks, with various levels of profitability and environmental impact. Alternative consensus techniques such as PoS are gaining traction.
